Stress, in its most basic form, is a force, pressure, or weight. Although our bodies are equipped to handle short-term stressors, chronic stress over long periods of time taxes the brain, body, and health to a great degree. Excessive stress can significantly impede the body’s ability to heal and regenerate. The immune-weakening effects of stress include recurring infections, slow wound healing, and becoming more susceptible to a cold or the flu.
Your body responds to stress through its stress-response system, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. The HPA axis produces specific hormones that help counteract the effects of short-term stress. Under normal conditions, cortisol is released in response to stress for a quick burst of energy, and to mobilize blood sugar and reduce inflammation. DHEA acts to counter-balance cortisol and binds receptors in the brain to promote relaxation and decreased pain. Prolonged stress can create an imbalance of cortisol and DHEA, and the long-term effects of cortisol can wreak havoc on the body.
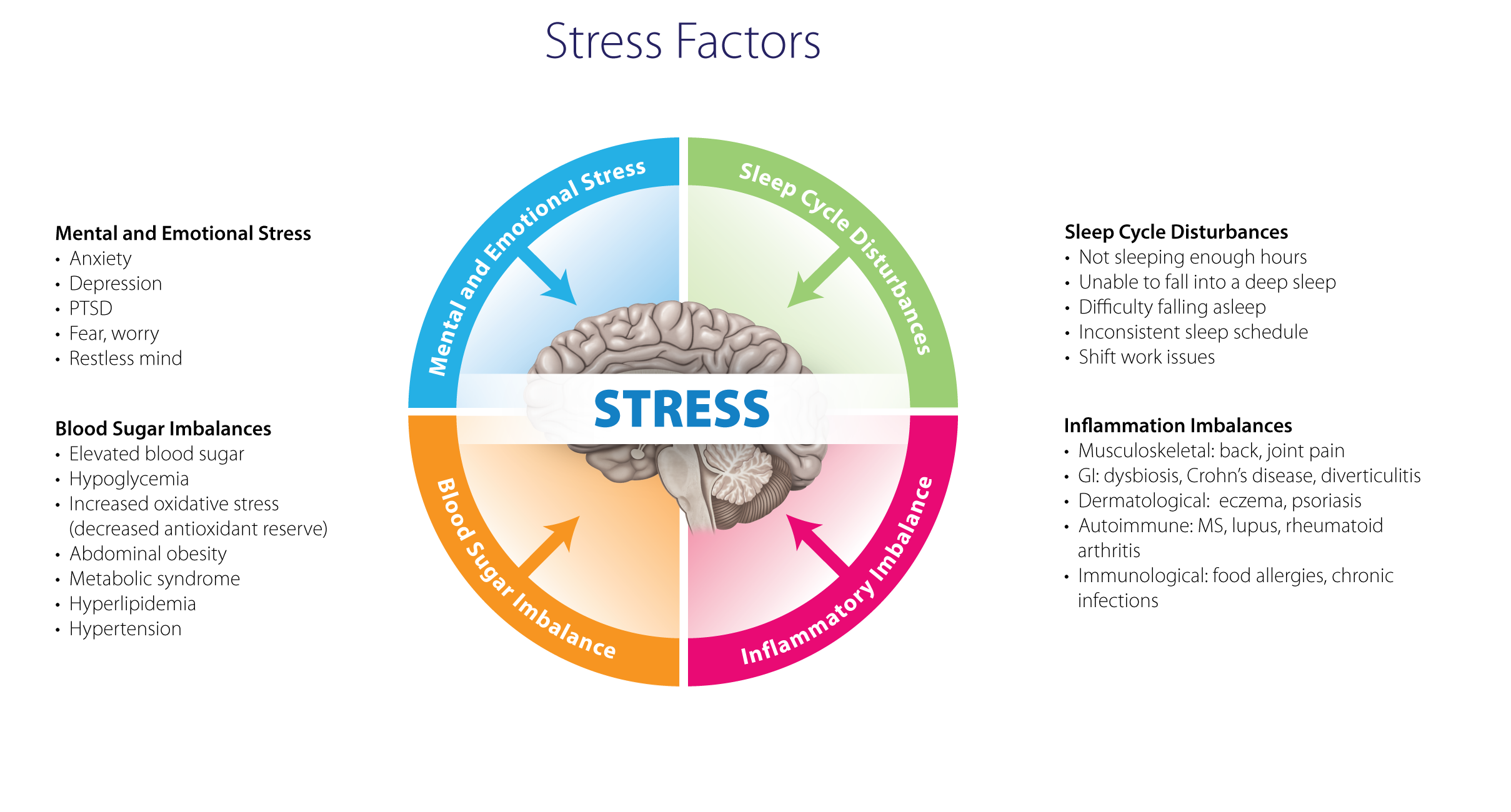
Chronic stress decreases the body’s ability to fight off infections. Chronic stress can also significantly increase inflammation in the body, leading to cellular, tissue and joint damage. Other indirect effects on the immune system are the unhealthy coping strategies people seek during periods of high stress. These include resorting to junk food, smoking or excessive drinking. Additionally, disruption of normal healthy habits such as exercise, sleep and healthy meal preparation can place even more burden on the body.
How to Mitigate the Effects of Stress
We are not able to avoid stress completely. Reducing your stress level as much as possible can be an important step in improving your health. Reduce the effects of stress with these tips:
- Identify stressors as well as steps you can take to change or eliminate these factors.
- Keep a thought and gratitude journal. Reframe negative thoughts and focus on those things for which you are grateful.
- Schedule adequate rest and downtime.
- Build relationships and avoid isolation when stress is high. Connecting with friends and family can offer emotional support.
- Exercise regularly, ideally in nature. Aerobic exercise releases endorphins in the brain to improve mood. Getting exposure to fresh air and sunlight can also help elevate feelings of well-being.
- Most importantly, seek professional counseling if your stress level has become overwhelming or unmanageable. Don’t be afraid to ask for help.
If you need additional support for reducing stress and the impact that it has on your body, please give Julian Healthcare a call to schedule an appointment. Schedule a free discovery call with Susan and see if our clinic would be a good fit for you!

